Introduction to Digital Marketing
Digital marketing is the practice of promoting products, services, or brands through digital channels and technologies. In today’s interconnected world, it’s an essential skill for businesses and individuals alike.
Key Components of Digital Marketing
Here are short descriptions for each of the Digital Marketing Strategies:
- Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
SEO is the process of optimizing websites and content to rank higher in organic search engine results, enhancing visibility and driving traffic without paid advertising. - Search Engine Marketing (SEM)
SEM involves using paid advertising to increase visibility on search engine results pages (SERPs), often through pay-per-click (PPC) campaigns. - Social Media Optimization (SMO)
SMO focuses on enhancing visibility and engagement on social media platforms by optimizing content and profiles for better interaction with users. - Social Media Marketing (SMM)
SMM involves actively promoting products or services on social media platforms through advertising, regular posting, and influencer campaigns to achieve marketing objectives. - Email Marketing
Email marketing uses email to promote products, services, or content, often targeting specific audiences to build brand awareness and drive sales. - Content Marketing
Content marketing involves creating and distributing valuable, relevant content to attract and retain a clearly defined audience, driving customer action without direct sales pitches. - Affiliate Marketing
Affiliate marketing is a strategy where individuals earn commissions by promoting other companies’ products or services, often through unique referral links. - Influencer Marketing
Influencer marketing involves partnering with influential individuals on social media or other platforms to promote products or services to their followers. - Mobile Marketing
Mobile marketing targets audiences through mobile devices, using strategies like SMS, apps, and mobile-specific advertising to reach users on-the-go. - Video Marketing
Video marketing uses video content to promote products, services, or brands, often distributed across various platforms like YouTube, social media, and websites. - Pay-Per-Click Advertising (PPC): Running targeted ad campaigns on search engines and social media platforms
- Funnel : In marketing, a funnel represents the customer journey, from initial awareness to becoming a paying customer, broken down into stages like awareness, consideration, and conversion.
- Digital Marketing Funnel : In digital marketing, a funnel represents the stages a customer goes through from initial awareness to becoming a paying customer, including stages like awareness, consideration, conversion, and retention.
The Digital Marketing Funnel
Understanding the customer journey is crucial in digital marketing. The typical funnel includes:
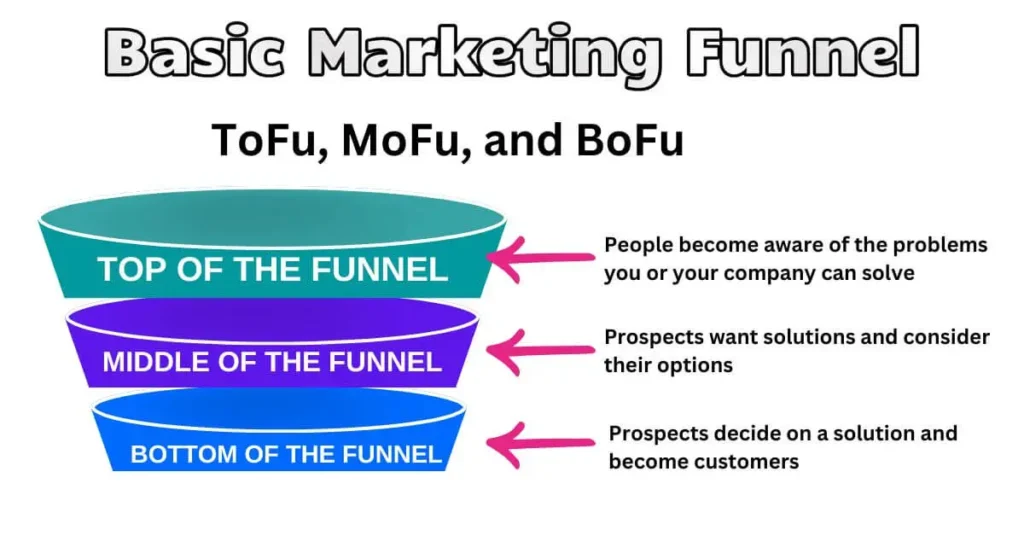
- Awareness
- Interest
- Consideration
- Intent
- Evaluation
- Purchase
Module 1: Fundamentals of Digital Marketing

Module 1.1 : Overview
Welcome to the world of digital marketing! In this module, we’ll explore why digital marketing matters and how to create effective strategies in today’s online world.
Digital Marketing is all about reaching and engaging customers through the internet, social media, and other digital platforms. It’s become crucial for businesses to master these skills as more people spend time online.
We’ll cover key concepts like:
- The basics of marketing and how they apply to digital channels
- Why understanding your customers is essential
- How to create a strong online presence
- The power of social media and content marketing
- Ways to measure your success using data and analytics
By the end of this module, you’ll be able to:
- Explain what digital marketing is and why it’s important
- Identify the main components of a digital marketing strategy
- Understand how digital marketing fits into overall business goals
- Use key terms like SEO, content marketing, and social media marketing
- Start planning your own digital marketing campaigns
We’ll use a Six-phase process to guide our learning:
- Planning
- Claiming your online space
- Creating content
- Uniting your efforts
- Advertising
- Analyzing results
Get ready to dive in and discover the exciting possibilities of digital marketing!
To make the most of this module:
- Watch all the videos
- Read the blog post for Module 1
- Complete the exercises to test your understanding
- Review the key terms and concepts
Let’s begin our journey into the world of digital marketing!
Watch the Video Here
M 1.2: For Module 1 : Terms You Should Know
Here’s a list of key terms for Module 1 with their definitions:
- Marketing strategy — A comprehensive, long-term plan that outlines how a business will achieve its marketing goals and objectives. It includes elements such as target audience, value proposition, brand messaging, and overall direction for marketing efforts.
- Marketing tactics — Specific actions or techniques used to implement the marketing strategy. These are short-term, adaptable activities like social media posts, email campaigns, or advertising that support the broader strategy.
- Metrics — Measurable indicators used to evaluate the performance and effectiveness of marketing efforts. Examples include conversion rates, click-through rates (CTR), and return on ad spend (ROAS).
- IP Address — A unique numerical identifier assigned to each device connected to a computer network. It allows devices to communicate with each other and looks like this: 211.101.89.0.
- URL (Uniform Resource Locator) — The web address of a specific resource on the Internet, including web pages, images, or files.
- Domain name — The human-readable address of a website, such as https://www.mit.edu/ or https://www.ama.org/. It’s part of the URL and typically consists of a name followed by a top-level domain (TLD).
- TLD (Top Level Domain) — The last segment of a domain name, such as .com, .org, or .ca, which indicates the purpose or geographic location of the website.
- Directory — A folder used to organize content on a website, often reflected in the URL structure.
- Digital marketing — The practice of promoting products, services, or brands through digital channels and technologies, including social media, search engines, email, and websites.
- Omnichannel approach — A marketing strategy that provides a seamless and consistent customer experience across all channels and touchpoints, both online and offline.
- Thin-slicing — The ability to make quick, accurate judgments based on limited information, often applied in digital marketing to understand consumer behavior.
- Crowdsourcing — The practice of obtaining ideas, content, or services by soliciting contributions from a large group of people, especially online communities.
- Digital analytics — The analysis of qualitative and quantitative data from digital sources to drive continuous improvement of the online customer experience and achieve desired outcomes.
M 1.3: Marketing and Digital Marketing
Marketing and Digital Marketing are two closely related concepts that are essential for modern businesses. Let’s explore these concepts in more detail:
Marketing: The Foundation
Marketing is a broad discipline that focuses on creating, communicating, and delivering value to customers. Dr. Philip Kotler, often referred to as the “Father of Modern Marketing,” defines marketing as:
“The science and art of exploring, creating, and delivering value to satisfy the needs of a target market at a profit. Marketing identifies unfulfilled needs and desires. It defines, measures, and quantifies the size of the identified market and the profit potential”[1].
This definition emphasizes several key aspects of marketing:
- Value creation: Developing products or services that meet customer needs.
- Target market: Identifying and focusing on specific groups of customers.
- Profit: Ensuring that marketing efforts lead to financial success for the organization.
- Market research: Understanding customer needs and market potential.
Marketing strategies typically involve the famous “4 Ps“:
- Product: What you’re selling
- Price: How much you’re charging
- Place: Where you’re selling it
- Promotion: How you’re communicating about it
Digital Marketing: Marketing in the Digital Age
Digital marketing is a subset of marketing that uses digital channels and technologies to reach and engage customers. A comprehensive definition of digital marketing is:
“A participatory layer of all media that allows users to self-select their own experiences, and affords marketers the ability to bridge media, gain feedback, iterate their message, and collect relationships”[2].
Key features of digital marketing include:
- Interactivity: Customers can actively engage with brands online.
- Precision targeting: Digital tools allow for highly specific audience segmentation.
- Measurability: Digital actions (clicks, views, purchases) can be tracked and analyzed.
- Real-time adaptation: Marketers can quickly adjust strategies based on immediate feedback.
The Relationship Between Marketing and Digital Marketing
Digital marketing is not separate from traditional marketing; rather, it’s an evolution and extension of marketing principles in the digital realm. Both share the core goal of connecting with customers and driving sales. However, digital marketing offers some unique advantages:
- Expanded reach: Digital channels allow businesses to connect with a global audience.
- Cost-effectiveness: Many digital marketing tactics are more affordable than traditional methods.
- Personalization: Digital tools enable highly personalized marketing messages.
- Data-driven decisions: The wealth of data available in digital marketing allows for more informed strategy adjustments.
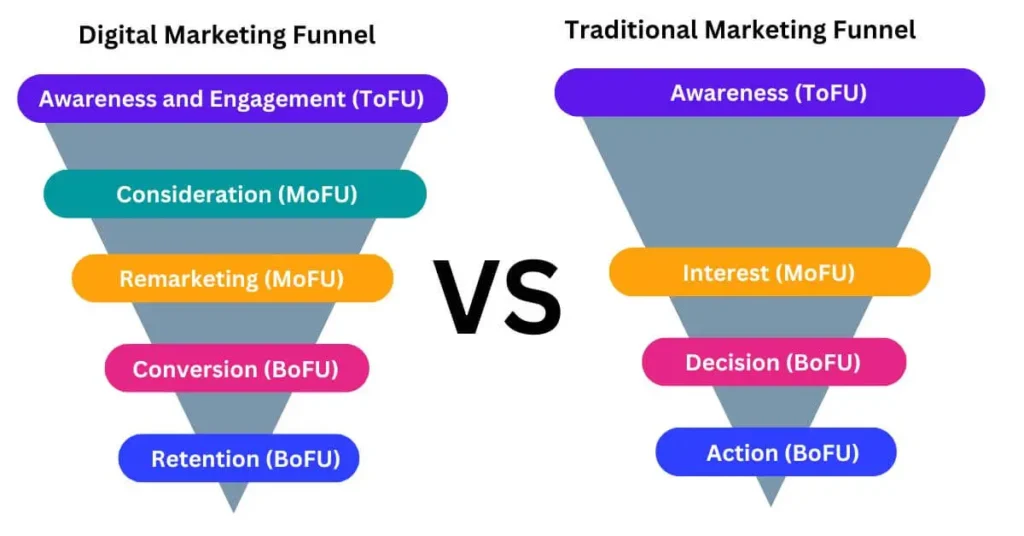
The Power of Digital Marketing
The digital landscape has transformed how businesses interact with customers. Some key impacts include:
- Consumer empowerment: Customers can easily research products, compare prices, and share experiences online.
- New product types: Digital technologies have enabled entirely new categories of products and services (e.g., apps, streaming content).
- Rapid feedback: Businesses can quickly gauge customer reactions and adjust their strategies accordingly.
- Omnichannel experiences: Digital marketing allows for seamless integration of various customer touchpoints.
In conclusion, while digital marketing is a specific application of marketing principles in the digital realm, it has become an indispensable part of overall marketing strategies for most businesses today. The key is to integrate digital marketing tactics with traditional marketing approaches to create a cohesive and effective marketing strategy.
References:
[1] Kotler, P. (2012). Marketing Management (14th ed.). Pearson.
[2] Stokes, R. & The Creative Minds of Red & Yellow. (2022). eMarketing: The Essential Guide to Marketing in a Digital World (6th ed.). Quirk eMarketing.
[3] American Marketing Association. (2017). Definitions of Marketing. Retrieved from https://www.ama.org/the-definition-of-marketing-what-is-marketing/
M 1.4: Digital Marketing – STRATEGY
Digital Marketing Strategy-Overview
Digital marketing is an extension of traditional marketing that operates in the digital realm. To understand how digital marketing connects to the broader marketing strategy process and the 4 Ps, let’s explore its integration.
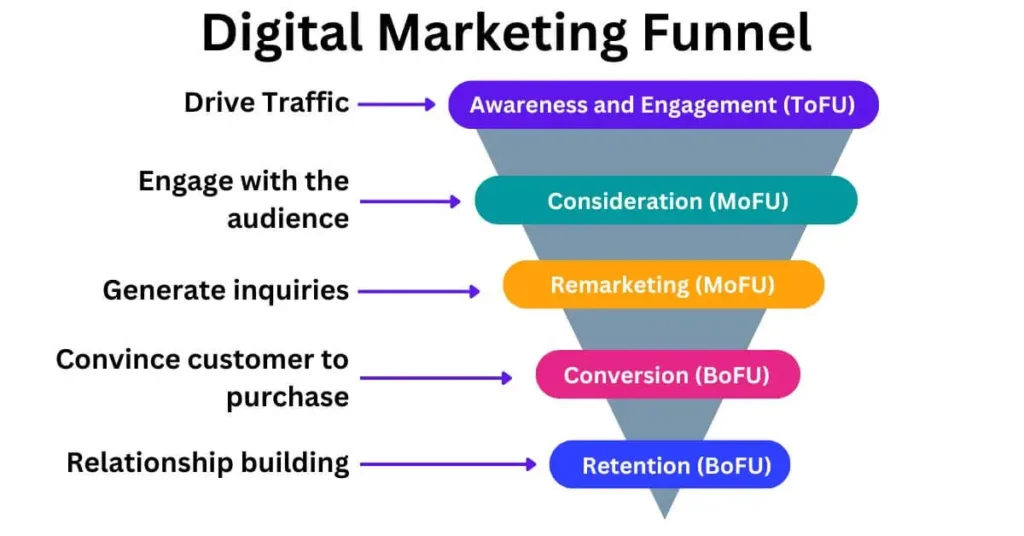
The Marketing Strategy- Process
A successful marketing strategy typically follows seven structured steps. These steps provide a foundation for both traditional and digital marketing strategies:
- Understanding the Customer
Begin by profiling your target audience. Identify their needs, wants, demographics, preferences, and behaviors. This understanding forms the basis of all marketing efforts. - Situational Analysis (SWOT)
Conduct a SWOT analysis to evaluate your business’s internal strengths and weaknesses, as well as external opportunities and threats. This step helps you identify areas to leverage or improve. - Researching the Competition
Study the market landscape using tools like Porter’s Five Forces to analyze both direct and indirect competitors. Understand what makes them successful and where gaps exist. - Marketing Network Development
Build a supply chain and distribution network by identifying intermediaries who can help deliver your product or service effectively. - Developing the Marketing Mix (4 Ps)
Strategically define your product, pricing, placement (distribution), and promotion to align with customer needs and business goals. - Designing and Executing Strategy
Implement your marketing plan by deploying targeted actions and tactics across chosen channels. - Reviewing and Revising
Continuously monitor performance metrics to evaluate the impact of your strategy. Revise tactics as needed based on data insights.
Digital Marketing Strategies & Tactics
Digital marketing amplifies traditional strategies by leveraging online tools and platforms to connect with audiences in innovative ways. Here are some core digital marketing strategies:
- Branding: Establish a recognizable identity across digital platforms.
- Social Media Marketing: Engage with audiences on platforms like Instagram, Facebook, TikTok, and LinkedIn.
- Content Marketing: Create valuable content (blogs, videos, infographics) to attract and retain customers.
- Email Marketing: Build relationships through personalized email campaigns.
- Video Production: Use video content to educate, entertain, or promote products.
- Search Engine Optimization (SEO): Optimize content to rank higher in search engine results.
- Web Design: Create user-friendly websites that enhance customer experiences.
- App Development: Build mobile applications for added convenience and engagement.
- Search Engine Marketing (SEM): Run paid ads on search engines to drive traffic.
One of the most significant advantages of digital marketing is the constant flow of feedback through measurable data such as clicks, likes, shares, and conversions. This allows marketers to make real-time adjustments for continuous improvement.
Digital Marketing and the 4 Ps
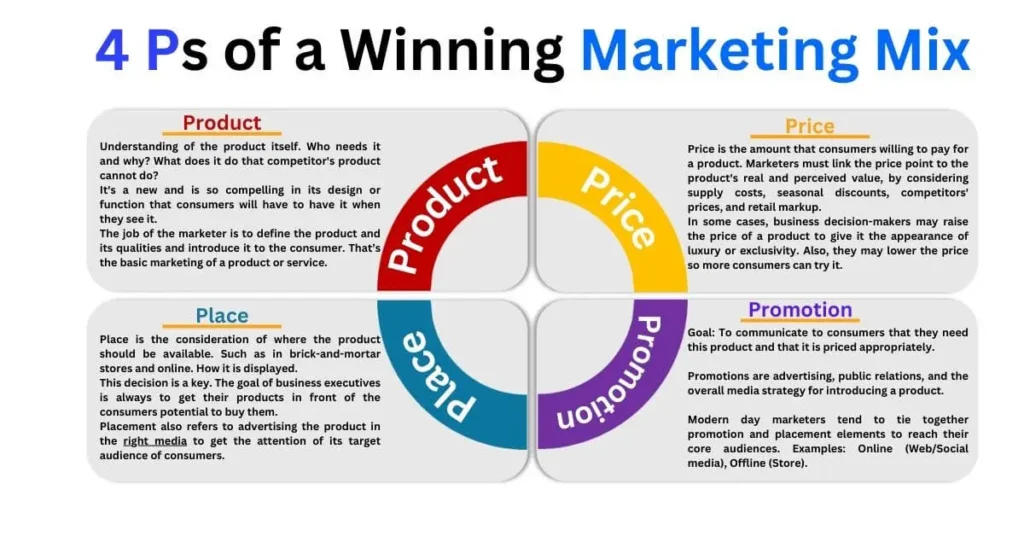
Digital Marketing Meets the 4 Ps
The 4 Ps—Product, Price, Place, Promotion—remain relevant in digital marketing but are adapted to fit the digital context:
- Product: In the digital world, products can include physical goods, services, or even digital assets like eBooks or software. Emphasize features that solve customer pain points.
- Price: Pricing strategies need flexibility for online consumers who can easily compare prices across competitors. Discounts or dynamic pricing models are common in e-commerce.
- Place: The concept of “place” shifts from physical stores to online platforms such as websites, marketplaces (e.g., Amazon), or social media channels.
- Promotion: Digital promotion leverages tools like social media advertising, influencer partnerships, email campaigns, and SEO to reach target audiences efficiently.
An Example: 4 Ps
Planning a Digital Marketing Campaign Using the 4 Ps
Imagine you’re tasked with promoting a new Basketball club using digital marketing:
How are you assigning each item related to Basketball Club in to 4 Ps? Here is how…
- Product: Highlight unique features like advanced Basketball courts, professional coaching sessions, or exclusive memberships.
- Price: Offer flexible pricing tiers (e.g., daily passes vs. annual memberships) with promotional discounts for early sign-ups.
- Place: Use a well-designed website with booking capabilities alongside social media pages for visibility.
- Promotion: Run targeted ads on Instagram and Google Ads; create engaging content like tutorials or behind-the-scenes videos of club activities.
Conclusion
Digital marketing reflects traditional marketing principles but adapts them for a highly interactive and measurable environment. By integrating strategies like branding, SEO, social media engagement, and data-driven decision-making into the 4 Ps framework, businesses can effectively connect with modern consumers in meaningful ways.
References (APA Style)
- Stokes, R., & The Creative Minds of Red & Yellow. (2018). eMarketing: The Essential Guide to Marketing in a Digital World (6th ed.). Quirk eMarketing.
- Shopify. (2023). What is a Digital Marketing Strategy? The Ultimate Guide. Retrieved from https://www.shopify.com
- HubSpot Blog Team. (2024). How to Create a Complete Marketing Strategy in 2025. Retrieved from https://blog.hubspot.com/marketing/marketing-strategy
M 1.5: Exercise 1 – Digital Marketing and the 4 Ps for a Baseball Club
Now, let’s do an exercise.
How would you use the 4 Ps in a digital marketing campaign for a new Baseball club? Can you construct the answer? Then read below.
Planning a digital marketing campaign for a new baseball club using the 4 Ps framework—Product, Price, Place, and Promotion—requires adapting traditional marketing strategies to the digital environment. Here’s how each “P” can be applied effectively:

1. Product
The product in this case is the baseball club itself, which includes its games, facilities, team experience, and any additional offerings like merchandise or memberships. To market the product digitally:
- Highlight Unique Features: Showcase what sets your baseball club apart, such as state-of-the-art facilities, family-friendly events, or star players.
- Content Creation: Share behind-the-scenes videos of players practicing, interviews with coaches, or highlights from previous games on platforms like Instagram and YouTube[2][4].
- Merchandising: Promote branded merchandise (caps, jerseys, etc.) through an e-commerce platform integrated into your website.
2. Price
Pricing strategies should be flexible and appealing to different audience segments. In the digital space:
- Dynamic Pricing: Offer early-bird discounts for tickets purchased online or group packages for families.
- Promotions: Use limited-time offers or flash sales promoted via email campaigns and social media ads to create urgency[3][6].
- Membership Tiers: Introduce tiered memberships with exclusive perks like VIP seating or access to special events.
3. Place
Place refers to how your baseball club is accessible to fans. In digital marketing:
- Website Optimization: Create a user-friendly website where fans can easily purchase tickets, view schedules, and learn about the team[1].
- Social Media Platforms: Leverage social media channels like Instagram, Facebook, TikTok, and Twitter to connect with fans and share updates[2][4].
- Mobile Apps: Develop a mobile app offering live game updates, ticket purchasing options, and exclusive fan content[2].
- Local SEO: Optimize your Google Business Profile with accurate information about your stadium’s location, hours, and contact details. Use local keywords to attract nearby audiences searching for events[1].
4. Promotion
Promotion is key to generating buzz around your baseball club. Digital promotion strategies include:
- Social Media Campaigns: Run interactive campaigns featuring player takeovers, fan contests (e.g., best game-day photo), or giveaways[2][4].
- Paid Advertising: Use targeted ads on platforms like Facebook and Instagram to promote upcoming games or special events. Paid ads ensure a broader reach and allow precise audience targeting based on demographics and interests[1][3].
- Email Marketing: Send personalized emails with updates about games, promotions on tickets or merchandise, and exclusive content like player interviews[2].
- Influencer Collaborations: Partner with local influencers to showcase their experiences at games or promote giveaways to their followers[2].
- Hashtag Campaigns: Create branded hashtags (e.g., #HomeRunExperience) that fans can use when sharing photos or videos from games[4].
Example Campaign Plan
Imagine launching a digital campaign for the baseball club’s opening day:
- Product: Share a teaser video of the team preparing for the season on Instagram Stories.
- Price: Offer a 20% discount on early-bird tickets purchased online.
- Place: Post game-day details on your website and link it across all social media platforms.
- Promotion: Run a contest where fans who tag your team in their posts using #OpeningDayBaseball get entered into a raffle for free merchandise.
Conclusion
By integrating the 4 Ps into your digital marketing strategy, you can effectively promote your baseball club while engaging fans in meaningful ways. The digital environment allows for real-time feedback and data-driven adjustments to ensure your campaign’s success.
References (APA Style)
- Sixth City Marketing. (2024). Digital Marketing for Minor League Baseball Teams. Retrieved from https://www.sixthcitymarketing.com
- My Front Office. (2025). 12 Innovative Digital Marketing Strategies for Minor League Sports. Retrieved from https://myfrontoffice.net
- Creatitive. (2024). Baseball Marketing: Knock Out Social Media Strategies. Retrieved from https://creatitive.com
- Elite Digital Agency. (2024). Digital Marketing Tips We Learnt From the Toronto Blue Jays. Retrieved from https://elitedigitalagency.com
M 1.6: Omnichannel Approach
What is the Omnichannel Approach?
The term “omnichannel” refers to a business strategy that integrates multiple customer touchpoints—both online and offline—into a unified, seamless experience. Unlike multichannel retail, where each channel operates independently, omnichannel retail ensures that customers can transition between channels effortlessly while enjoying consistent service quality, pricing, and promotions.
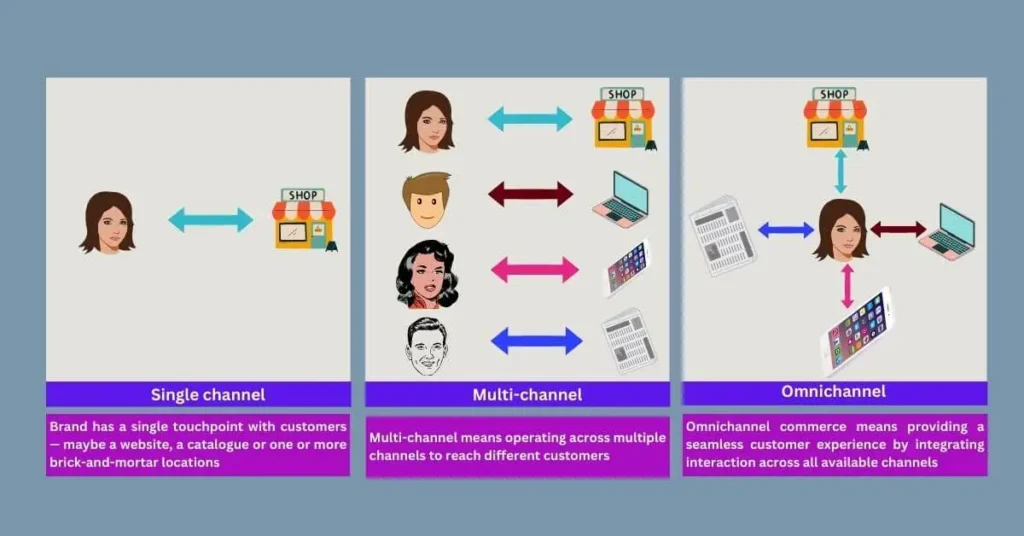
Single channel:
Brand has a single touchpoint with customers — maybe a website, a catalogue or one or more brick-and-mortar locations
Multi-channel:
Multi-channel means operating across multiple channels to reach different customers
Omnichannel:
Omnichannel commerce means providing a seamless customer experience by integrating interaction across all available channels
For example, a customer might browse products on their smartphone, check inventory at a local store, and complete the purchase in person—all while receiving a cohesive experience across platforms. This strategy leverages centralized data management to personalize interactions and optimize operations, resulting in higher customer satisfaction, loyalty, and retention rates[1][3][5].
CASE STUDY: Walmart’s Omnichannel Approach

Walmart is a leading example of the successful implementation of an omnichannel strategy. The company has seamlessly integrated its physical stores with its eCommerce platforms to provide customers with convenience and flexibility. Walmart’s omnichannel offerings include:
- Pickup and Delivery Options: Customers can order online and pick up their purchases at one of Walmart’s 8,000+ pickup locations or use same-day delivery services available at over 4,300 stores.
- In-Home Delivery: Walmart offers in-home delivery for groceries and other essentials.
- Ship-from-Store: Orders placed online are fulfilled directly from local store inventories to ensure faster delivery.
- Digital Pharmacy Fulfillment: Customers can manage prescriptions online or via the Walmart app.
- Sam’s Club Features: Through its membership-based warehouse club segment, Walmart provides curbside pickup, mobile Scan & Go (to skip checkout lines), and delivery-from-club options.
- Technology Integration: Walmart uses tools like the Scan & Go app to enhance the shopping experience by allowing customers to scan items as they shop[2][6][8].
These innovations demonstrate Walmart’s commitment to providing a customer-centric experience that integrates its vast store network with cutting-edge technology.
Case Study Questions
1. Why was it useful for executives to understand how digital marketing spend impacted overall sales?
Answer: Understanding the impact of digital marketing spend on overall sales helps executives allocate resources effectively. It enables them to identify which channels drive the most revenue and optimize campaigns for better ROI.
2. Describe what an ‘omnichannel’ approach means.
Answer: An omnichannel approach ensures a seamless customer experience across all interaction points—whether online (e.g., websites, apps) or offline (e.g., physical stores). It integrates these channels so customers can transition between them effortlessly while enjoying consistent service.
3. What did Walmart’s omnichannel approach look like?
Answer: Walmart’s omnichannel approach included integrating its physical stores with its digital platforms. Customers could research products online before visiting stores or make purchases online with options for in-store pickup or home delivery. This strategy aimed to enhance convenience and drive sales.
4. What was the key learning for Walmart after successfully completing the experiment to increase sales?
Answer: Walmart learned that integrating digital marketing efforts with physical retail locations significantly boosted sales by enhancing customer convenience and satisfaction. The experiment underscored the importance of aligning all channels into a cohesive strategy.
5. How does Walmart leverage its store footprint in its omnichannel strategy?
Answer: Walmart uses its physical stores as fulfillment centers for online orders through options like ship-from-store and local pickup. This approach optimizes inventory placement, reduces delivery times, and lowers costs compared to traditional distribution center fulfillment.
6. What benefits does an omnichannel strategy offer businesses like Walmart?
Answer: Benefits include increased customer satisfaction through personalized experiences, improved operational efficiency via centralized data management, higher sales from seamless transitions between channels, and enhanced brand loyalty due to consistent service quality.
Conclusion
The omnichannel approach is transforming how businesses engage with customers by creating unified experiences across all platforms. Walmart’s strategy exemplifies this by integrating physical stores with eCommerce capabilities through innovative services such as same-day delivery, in-home delivery, and ship-from-store options. Businesses adopting such strategies can expect improved customer retention, operational efficiency, and competitive advantages in today’s retail landscape.
References (APA Style)
- Frost & Sullivan. (2020). Omnichannel Retailing: Seamless Customer Experiences Across Channels.
- Stokes, R., & The Creative Minds of Red & Yellow. (2018). eMarketing: The Essential Guide to Marketing in a Digital World (6th ed.). Quirk eMarketing.
- BigCommerce Team. (2025). Comprehensive Guide for Omnichannel Retail Success. Retrieved from https://www.bigcommerce.com
- PYMNTS Team. (2024). Walmart Grows Omnichannel Capabilities for Shoppers Seeking Convenience. Retrieved from https://www.pymnts.com
- Shopify Team. (2024). Omnichannel Retailing Strategy: Benefits and Examples. Retrieved from https://www.shopify.com
- Magestore Team. (2024). What is Omnichannel Retailing? Basics Explained. Retrieved from https://www.magestore.com
Next Topic is….
M 1.7: The TCERO Model: A Comprehensive & STRUCTURED Approach to Digital Marketing
In the ever-evolving landscape of digital marketing, businesses need a structured approach to navigate the complexities of online engagement and customer retention. The TCERO model, an extension of the well-established TCEO framework, offers a comprehensive strategy that encompasses the entire customer journey. This blog post will explore the five pillars of the TCERO model: Think, Create, Engage, Retain, and Optimize.
5- Day ONLINE BUSINESS BUILDER CHALLENGE
This module laid the groundwork for understanding the digital marketing landscape, providing students with the knowledge and tools to navigate the complexities of marketing in the digital age. The concepts covered here will serve as a foundation for more advanced digital marketing strategies and tactics in subsequent modules. This is the Part 1 of Module 1.
A Bonus Tip: Digital Marketing Skills-Fast Track, Earn while Learning
If you want to learn Digital Marketing skills through a fast track and earn a commission here is a way to do that. Join Legendary Marketer 5 Day Business Builder Challenge. You can earn while learning.
They’re providing EVERY SINGLE STUDENT of the 5-Day Learn Launch Lead Challenge a dedicated advisor to go through the challenge WITH you.
I followed that and now I am an affiliate. If you sign up with the following link I may get a commission. No extra cost to you. Instead you may get discounts. The starter course is just $5. Go through the program with an advisor. It’s a great opportunity and beneficial.
Note: This is the end of Part 1 of Module 1. Module 1 is the foundation. As it is called MODULE 1: FUNDAMENTALS OF DIGITAL MARKETING, this module set the foundation. As you may remember we have 3 parts for this module. If you haven’t read Part 2 and part 3 yet, please check the following links to go there. Thank you so much for reading my blog posts and going through these lessons.
Go to part 2 from here.
Go to part 3 from here. Just Click here to go to part 3.


